THE VALUE OFCitiesWithNature
Nature provides diverse life-supporting and life-enhancing contributions to people in cities and towns. These gifts from nature make human life both possible and worth living. All cities critically depend on healthy interconnected ecosystems within and around them, so it is essential that nature is fully integrated into urban planning and development. There is a growing urgency for collective and large scale action to protect the biodiversity in and around cities to prevent irreversible loss and damage to the natural systems we depend on.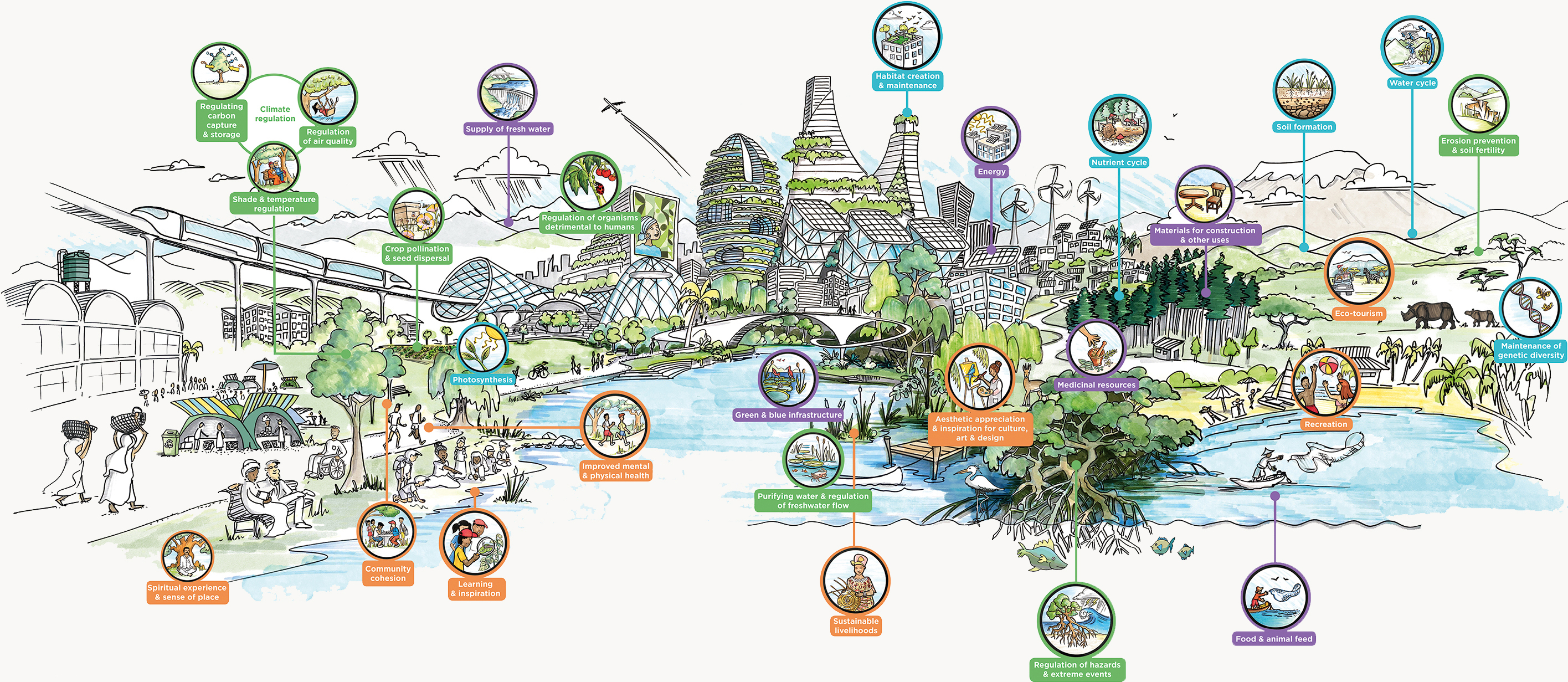

Regulating carbon capture & storage

As trees and plants grow, they remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere by absorbing and storing it in their tissues.
Regulation of air quality

Trees and other plants play an important role in regulating air quality by removing pollutants from the atmosphere thereby improving human well-being.
Shade & temperature regulation

Trees and vegetation cool surface and air temperatures by providing shade and through evapotranspiration.
Spiritual experience & sense of place

Nature creates opportunities for people to develop a sense of place, belonging, purpose, rootedness or connectedness, associated with different elements of the natural world (e.g. cultural and heritage landscapes, sounds, scents and sights associated with childhood experiences, iconic animals, trees or plants). Nature also provides the basis for rituals and celebrations as well as for narratives and myths.
Community cohesion

Green spaces provide people with opportunities for socializing with family and friends, as well as create social-cohesion experiences. In addition, this provides a health benefit through social interaction.
Crop pollination & seed dispersal

Nature and organisms facilitate plant reproduction through the movement of pollen among flowers, so ensuring fruit production. Organisms also facilitate the dispersal of seeds, larvae or spores of other organisms to ensure plant population viability and survival.
Supply of fresh water

Nature plays a vital role in the global water cycle, as it regulates the flow and purification of water through the filtration of particles, pathogens, excess nutrients, and other chemicals.
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is the process by which plants combine carbon dioxide (removed from the atmosphere) with water and light energy from the sun to produce glucose and oxygen.
Learning & inspiration

The natural environment provides for the development of capabilities that allow humans to prosper through education, learning and acquiring knowledge, developing skills for well-being, scientific information and technological design (e.g. biomimicry).
Improved mental & physical health

Exposure to the natural environment can have a range of physical, psychological and social benefits that can contribute to improved physical and mental health. Walking and playing sports in green space is a good form of exercise and also creates space for people to relax.
Regulation of organisms detrimental to humans

The regulation of pests, pathogens, predators, competitors, etc. that affect humans, plants and animals is facilitated by nature. Ecosystems regulate pests and diseases through the activities of predators and parasites. Organisms including birds, bats, frogs, flies and fungi all act as natural controls.
Habitat creation & maintenance

Ecosystems provide different habitats that can be essential for a species’ life cycle. Habitats provide the necessary ecological conditions that an individual plant or animal needs to survive, including food, water, and shelter.
Green & blue infrastructure

Green & blue infrastructure is an interconnected network of natural and semi-natural landscape elements, including green and open spaces and water bodies. It provides a number of benefits including enhanced water security, reduced risk of flooding, improved air pollution and green space for recreation and wildlife.
Purifying water & regulation of freshwater flow

Nature regulates the flow and purification of water through the filtration of particles, pathogens, excess nutrients, and other chemicals thereby improving the quality of water used directly (e.g. for drinking) or indirectly (e.g. for irrigation purposes).
Sustainable livelihoods

Nature provides many of the resources (e.g. crops) and materials (e.g. wood) needed to sustain livelihoods and economic activities. Many poorer people are directly dependent on nature for their survival and trade.
Aesthetic appreciation and inspiration for culture, art & design

Natural landscapes, biodiversity and ecosystems have been the source of inspiration for much of our art, culture and design.
Energy

The sun’s energy warms the earth’s surface and can be used to produce cleaner, greener solar energy to power cities.
Nutrient cycle

Nutrient cycling is one of the most important processes that occurs in an ecosystem. The nutrient cycle describes the use, movement, and recycling of nutrients in the environment.
Nutrients move from the physical environment into living organisms and are then recycled back into the environment.
Medicinal resources

Ecosystems and biodiversity provide plants used as medicines, and provide many of the raw materials for the pharmaceutical industry used for medicinal and veterinary purposes.
Regulation of hazards & extreme events

Nature and living organisms create buffers (e.g. coastal mangroves) against extreme weather events or natural hazards including floods, storms, tsunamis and landslides, thereby preventing possible damage to the landscape and people within the region.
Materials for construction & other uses

Nature provides a great diversity of materials for construction, fuel, clothing and printing (e.g. wood, biofuels, fibers, paper) that are directly derived from wild and cultivated plant species.
Soil formation

Nature provides for the formation and maintenance of soil structure and processes (such as decomposition and nutrient cycling) that underlie the continued fertility of soils, which supports soil micro-organisms and plant growth.
Eco-tourism

Nature plays an important role for many kinds of tourism which in turn provides substantial economic benefits and is a vital source of income for many countries. Cultural and eco-tourism also educates people about the importance of ecosystems and biodiversity.
Recreation

Green and open spaces provide opportunities for activities that are physically and psychologically beneficial, for example recreation, relaxation, leisure, tourism and aesthetic enjoyment based on the close contact with nature (e.g. hiking, playing sports, bird watching, snorkeling, gardening).
Food & animal feed

Nature allows for the production of food from wild, managed, or domesticated organisms. Nature also produces feed for domesticated animals (e.g. livestock, work and support animals and pets) and for aquaculture.
Maintenance of genetic diversity

Nature provides for the maintenance of genetic diversity, which is the variety of genes between and within species populations. Genetic diversity facilitates the health and viability of populations of living beings.
Erosion prevention & soil fertility

Vegetation cover provides for sediment retention and erosion control as well as soil formation and maintenance of soil structure and processes (such as decomposition and nutrient cycling) that underlie the continued fertility of soils important to support plant growth.
Water cycle
Nature helps maintain the water cycle that involves the continuous circulation of water in the earth-atmosphere system. It helps to regulate the flow and purification of water, while vegetation (e.g. forests) also influence the quantity of water available locally.
TANGIBLE THINGS FROM NATURE THAT MEET HUMAN NEEDS
BENEFITS OBTAINED FROM THE PROCESSES THAT REGULATE THE NATURAL ENVIRONMENT
NATURES GIFTS THAT ENRICH OUR LIVES
SUPPORTING THE LONG-TERM HEALTH OF THE PLANT
Also see our value of wetlands for cities poster

Barcelona City Council
SPAIN
Municipality of Belo Horizonte
BRAZIL
City of Bonn
GERMANY
Bulawayo City Council
ZIMBABWE
Municipality of Campinas
BRAZIL
City of Cape Town
SOUTH AFRICA
City of Dar es Salaam
TANZANIA
Eden District Municipality
SOUTH AFRICA
Entebbe Municipal Council
UGANDA
eThekwini Metropolitan Municipality
SOUTH AFRICA
Knysna Local Municipality
SOUTH AFRICA
City of Malmö
SWEDEN
City of Melbourne
AUSTRALIA
Pamplemousses District
MAURITIUS
Municipality of the Metropolitan District of Quito
ECUADOR
Ruwa Local Board
ZIMBABWE
Santa Fe Municipality
ARGENTINA
Thabazimbi Local Municipality
SOUTH AFRICA
City of Tshwane
SOUTH AFRICAWHAT IS
CitiesWithNature?
CitiesWithNature is a unique initiative that recognizes and enhances the value of nature in and around cities across the world.
It provides a shared platform for cities and their partners to engage and connect, working with shared commitment towards a more sustainable urban world.

Why do we need nature in cities?
All cities, large and small, critically depend on healthy interconnected ecosystems within and around them, so it is essential that nature is fully integrated into urban planning and development. Nature provides diverse life-supporting and life-enhancing contributions to people in cities.
Join CitiesWithNature
These gifts from nature make human life both possible and worth living. There is a growing urgency for collective and large-scale action to protect the biodiversity in and around cities to prevent irreversible loss and damage to the natural systems we depend on.
CitiesWithNaturePARTNERS
CitiesWithNature is brought to you by founding partners ICLEI, TNC and IUCN, along with supporting bodies such as the CBD and other international partners.
Contact us today if your organization would like to become a partner


